List of Goods Produced by Child Labor or Forced Labor
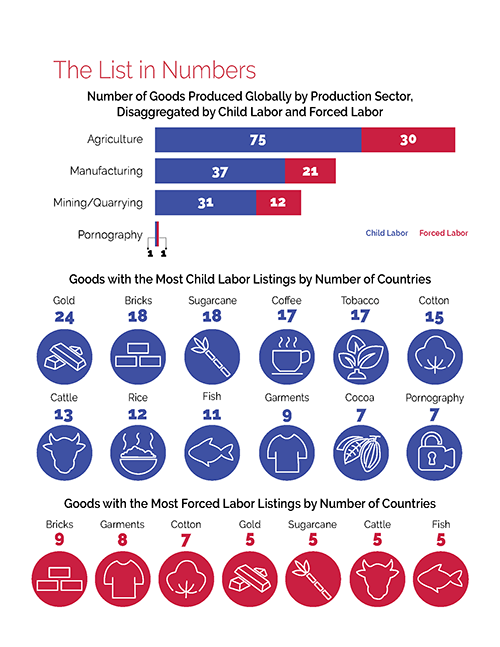
The Bureau of International Labor Affairs (ILAB) maintains a list of goods and their source countries which it has reason to believe are produced by child labor or forced labor in violation of international standards, as required under the Trafficking Victims Protection Reauthorization Act (TVPRA) of 2005 and subsequent reauthorizations. The List of Goods Produced by Child Labor or Forced Labor comprises 159 goods from 78 countries and areas, as of September 28, 2022.
ILAB maintains the List primarily to raise public awareness about forced labor and child labor around the world and to promote efforts to combat them; it is not intended to be punitive, but rather to serve as a catalyst for more strategic and focused coordination and collaboration among those working to address these problems.
Publication of the List has resulted in new opportunities for ILAB to engage with foreign governments to combat forced labor and child labor. It is also a valuable resource for researchers, advocacy organizations and companies wishing to carry out risk assessments and engage in due diligence on labor rights in their supply chains.
The countries on the List span every region of the world. The most common agricultural goods listed are sugarcane, cotton, coffee, tobacco, cattle, rice, and fish. In the manufacturing sector, bricks, garments, textiles, footwear, carpets, and fireworks appear most frequently. In mined or quarried goods, gold, coal and diamonds are most common.
ILAB published the initial TVPRA List in 2009 and updated it annually through 2014, following a set of procedural guidelines that were the product of an intensive public consultation process. ILAB now updates and publishes the List every other year, pursuant to changes in the law.
Procedural Guidelines
On January 25, 2024, ILAB's Office of Child Labor, Forced Labor, and Human Trafficking published Procedural Guidelines for the development and maintenance of the List of Goods from countries produced by child labor or forced labor in violation of international standards.
| Country/Area | Good Sort ascending | Exploitation Type |
|---|---|---|
| Congo, Democratic Republic of the (DRC) | There are reports that children ages 5-17 are forced to work in the production of coltan, or tantalum ore, in some mines in the Democratic Republic of the Congo. Reports from the U.S. Department of State and NGOs state that many children have been identified working in conditions of forced labor in the mines in Eastern Congo, particularly in North and South Kivu. Some children are forced to work at the mines with their families in situations of bonded labor, while other children are sent away to the mines by their parents to pay off the family's debt. These children are paid little, if at all. In addition, many mines are controlled by military officers or armed groups, which are known to round up villagers, including children, at gunpoint and force them to work with threats of violence. These forcibly-recruited children do not have freedom of movement and do not receive payment for their work. |
Child Labor, Forced Labor |
| Paraguay | There is evidence that children ages 5 to 17 grow sweet potatoes in Paraguay. In 2016, the Government of Paraguay published representative results from the Survey of Activities of Rural Area Children and Adolescents 2015. The survey considers a working child to be engaged in child labor if the child is below the minimum age for employment of 14 or the child is performing work that is hazardous according to national legislation. The survey estimates that 301,827 children ages 5 to 17 perform hazardous work in rural areas of Paraguay and indicates that children working in agriculture experience accidents and illnesses, including from using dangerous tools and handling chemicals. According to the survey, almost 13 percent of Paraguayan children engaged in child labor in agriculture do not attend school. The survey estimates that 8,143 child laborers grow sweet potatoes throughout rural areas in Paraguay. Approximately 4,912 of child laborers growing sweet potatoes are below the minimum age for employment in Paraguay. The survey indicates that more boys than girls are engaged in child labor producing sweet potatoes. The release of this survey demonstrates the Government of Paraguay’s commitment to addressing child labor and its acknowledgement that data collection is vital to the design and implementation of sound policies and programs. |
Child Labor |
| Pakistan | Child Labor | |
| Burma | Forced Labor | |
| Belize | Child Labor | |
| Bolivia | There are reports that children are forced to produce sugarcane in Bolivia. Based on the most recently available data from the ILO, it is estimated that almost a quarter of the migrants working in the sugarcane harvest are children under age 14, of which many are working in conditions of forced labor Many children work with their families under conditions of bonded labor. Entire families, including children, live in accommodations provided by the employer; this dependence on the employer increases their vulnerability to forced labor. The families receive little payment if any, and lodging and food expenses are deducted from their paychecks. Some children inherit the debt of their parents if their parents pass away or stop working, and remain bonded and able to be sold to a different employer. |
Child Labor, Forced Labor |
| Brazil | There is evidence that children ages 14 to 17 cultivate sugarcane in Brazil. Brazilian law prohibits all children under age 18 from producing sugarcane. Based on an analysis of the Government of Brazil’s 2015 National Household Survey, an estimated 5,503 child laborers cultivate sugarcane. Individuals, including children, who work in sugarcane production are exposed to long hours and high temperatures, and lack protective equipment. The release of this survey demonstrates the Government of Brazil’s commitment to addressing child labor and its acknowledgement that data collection is vital to the design and implementation of sound policies and programs. |
Child Labor, Forced Labor |
| Burma | There are reports that children are forced to work in the production of sugarcane in Burma. Forced child labor is found in the Thaton District, and particularly in areas near military camps. An NGO study documents villagers, including children, mobilized by the dozens each day from multiple villages to work during labor intensive times of the sugarcane production. The children are forced to cut trees and dig out the stumps to prepare the fields, plant the sugarcane, then mill and boil the sugarcane after it is harvested. They are not paid for their work. |
Child Labor, Forced Labor |
| Cambodia | There are reports that children ages 5 to 17 produce sugarcane in Cambodia. Child labor in the sugarcane sector occurs on both commercial plantations and smallholder farms. Children from families that have lost land through concessions to sugar companies are particularly vulnerable to exploitative labor on plantations. According to international organizations, NGOs, and media reports, child labor in the Cambodian sugarcane sector is a widespread concern, with numerous incidents reported across the country, including reports of hundreds of children cutting cane on plantations in the Koh Kong province. Children laboring in the sugarcane fields often work long hours under the hot sun and report difficulty breathing, headaches, and dizziness as a result. Child workers in this sector perform hazardous tasks such as carrying heavy bundles of sugarcane, using dangerous tools, and spraying toxic pesticides. Many children incur injuries on the job, including skin infections and cuts from sharp cane leaves or knives. |
Child Labor |
| Colombia | Child Labor |
your hand? Download ILAB's Sweat & Toil App today!
Are you a company looking to fight child labor and forced labor in supply
chains?