List of Goods Produced by Child Labor or Forced Labor
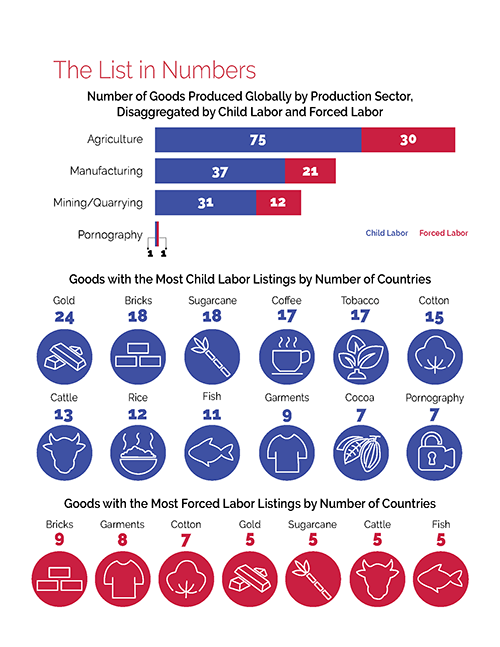
The Bureau of International Labor Affairs (ILAB) maintains a list of goods and their source countries which it has reason to believe are produced by child labor or forced labor in violation of international standards, as required under the Trafficking Victims Protection Reauthorization Act (TVPRA) of 2005 and subsequent reauthorizations. The List of Goods Produced by Child Labor or Forced Labor comprises 159 goods from 78 countries and areas, as of September 28, 2022.
ILAB maintains the List primarily to raise public awareness about forced labor and child labor around the world and to promote efforts to combat them; it is not intended to be punitive, but rather to serve as a catalyst for more strategic and focused coordination and collaboration among those working to address these problems.
Publication of the List has resulted in new opportunities for ILAB to engage with foreign governments to combat forced labor and child labor. It is also a valuable resource for researchers, advocacy organizations and companies wishing to carry out risk assessments and engage in due diligence on labor rights in their supply chains.
The countries on the List span every region of the world. The most common agricultural goods listed are sugarcane, cotton, coffee, tobacco, cattle, rice, and fish. In the manufacturing sector, bricks, garments, textiles, footwear, carpets, and fireworks appear most frequently. In mined or quarried goods, gold, coal and diamonds are most common.
ILAB published the initial TVPRA List in 2009 and updated it annually through 2014, following a set of procedural guidelines that were the product of an intensive public consultation process. ILAB now updates and publishes the List every other year, pursuant to changes in the law.
Procedural Guidelines
On January 25, 2024, ILAB's Office of Child Labor, Forced Labor, and Human Trafficking published Procedural Guidelines for the development and maintenance of the List of Goods from countries produced by child labor or forced labor in violation of international standards.
| Country/Area | Good | Exploitation Type |
|---|---|---|
| Zambia | Child Labor | |
| Bangladesh | Child Labor | |
| India | Child Labor | |
| Pakistan | Child Labor | |
| China | There are reports of glove factories forcibly training and employing 1,500 to 2,000 ethnic minority adult workers with the government’s support. Victim testimonies, news media, and think tanks report that factories, including for gloves, frequently engage in coercive recruitment; limit workers’ freedom of movement and communication; and subject workers to constant surveillance, retribution for religious beliefs, exclusion from community and social life, and isolation. Further, reports indicate little pay, mandatory Mandarin lessons, ideological indoctrination, and poor living conditions. In some instances, workers have been reported to be subject to torture. More broadly, according to varied estimates, at least 100,000 to hundreds of thousands of Uyghurs, ethnic Kazakhs, and other Muslim minorities are being subjected to forced labor in China following detention in re-education camps. In addition to this, poor workers in rural areas may also experience coercion without detention. Workers are either placed at factories within the Xinjiang Uyghur Autonomous Region, where the camps are located, or transferred out of Xinjiang to factories in eastern China. |
Forced Labor |
| Mauritania | Child Labor | |
| Paraguay | There is evidence that children ages 5 to 17 raise goats in Paraguay. In 2016, the Government of Paraguay published results from the Survey of Activities of Rural Area Children and Adolescents 2015, a representative survey of children’s work in rural areas. The survey considers a working child to be engaged in child labor if the child is below the minimum age for employment of 14 or the child is performing work that is hazardous according to national legislation. The survey estimates that 301,827 children ages 5 to 17 perform hazardous work in rural areas of Paraguay and indicates that children working in agriculture experience accidents and illnesses, including from using dangerous tools and handling chemicals. According to the survey, almost 13 percent of Paraguayan children engaged in child labor in agriculture do not attend school. The survey estimates that 8,584 child laborers raise goats throughout rural areas in Paraguay. Approximately 4,714 child laborers raising goats are below the minimum age for employment in Paraguay. The survey indicates that more boys than girls are engaged in child labor in goat raising. The release of this survey demonstrates the Government of Paraguay’s commitment to addressing child labor and its acknowledgement that data collection is vital to the design and implementation of sound policies and programs. |
Child Labor |
| Bolivia | Child Labor | |
| Burkina Faso | There are reports that children are forced to mine gold in the Sahel region of Burkina Faso. According to a report by the ILO containing the most recently available data, in the combined Sahel regions of Burkina Faso and Niger, up to 30-50 percent of the gold mine workforce is comprised of children; most are under the age of 15, and some work under conditions of forced labor. Some children from around the country are trafficked to mines in the country's Ioba, Oudalan, Passore, and Sissili provinces. These children work in small informal mines that are located in remote rural areas and mostly operate on a seasonal basis. The children, beginning between ages 12 and 14, are forced to work in hazardous conditions digging, breaking rocks, transporting, washing, and pounding the gold, including work underground in narrow shafts. These children receive little or no payment, with many receiving wage deductions for lodging and food expenses. |
Child Labor, Forced Labor |
| Cameroon | There are reports that children are involved in the mining of gold in eastern Cameroon. Children often mine alongside their families in artisanal mines, and reports indicate that their ages range from under age 10 to 17. Sometimes children mine gold by themselves for sale on the black market. Evidence of child labor has been found in Batouri and Kambele, near the border with the Central African Republic. Reports indicate that thousands of children in Kambele work in artisanal gold mining, while in nearby Batouri, roughly 90 percent of children participate in gold mining. Children mine in hazardous conditions, including standing in stagnant water, working underground, and using mercury to extract the gold dust. Many children leave school to work in gold mining, and a report indicates that over 75 percent of the students in one school stopped attending school to mine gold. |
Child Labor |
your hand? Download ILAB's Sweat & Toil App today!
Are you a company looking to fight child labor and forced labor in supply
chains?