List of Goods Produced by Child Labor or Forced Labor
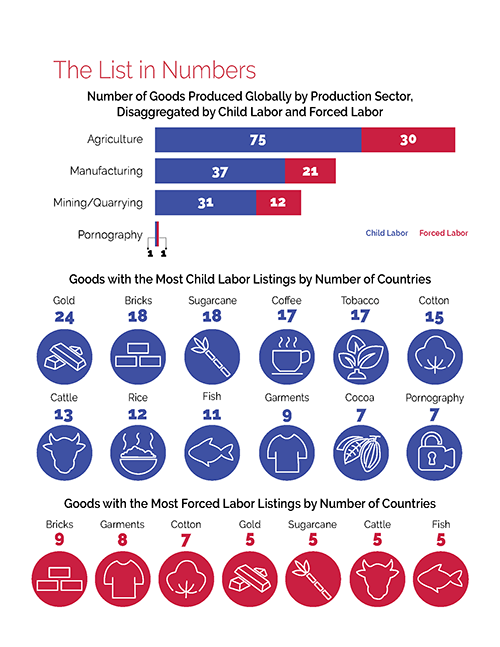
The Bureau of International Labor Affairs (ILAB) maintains a list of goods and their source countries which it has reason to believe are produced by child labor or forced labor in violation of international standards, as required under the Trafficking Victims Protection Reauthorization Act (TVPRA) of 2005 and subsequent reauthorizations. The List of Goods Produced by Child Labor or Forced Labor comprises 159 goods from 78 countries and areas, as of September 28, 2022.
ILAB maintains the List primarily to raise public awareness about forced labor and child labor around the world and to promote efforts to combat them; it is not intended to be punitive, but rather to serve as a catalyst for more strategic and focused coordination and collaboration among those working to address these problems.
Publication of the List has resulted in new opportunities for ILAB to engage with foreign governments to combat forced labor and child labor. It is also a valuable resource for researchers, advocacy organizations and companies wishing to carry out risk assessments and engage in due diligence on labor rights in their supply chains.
The countries on the List span every region of the world. The most common agricultural goods listed are sugarcane, cotton, coffee, tobacco, cattle, rice, and fish. In the manufacturing sector, bricks, garments, textiles, footwear, carpets, and fireworks appear most frequently. In mined or quarried goods, gold, coal and diamonds are most common.
ILAB published the initial TVPRA List in 2009 and updated it annually through 2014, following a set of procedural guidelines that were the product of an intensive public consultation process. ILAB now updates and publishes the List every other year, pursuant to changes in the law.
Procedural Guidelines
On January 25, 2024, ILAB's Office of Child Labor, Forced Labor, and Human Trafficking published Procedural Guidelines for the development and maintenance of the List of Goods from countries produced by child labor or forced labor in violation of international standards.
| Country/Area | Good Sort ascending | Exploitation Type |
|---|---|---|
| Pakistan | Forced Labor | |
| Congo, Democratic Republic of the (DRC) | There are reports that children ages 5-17 are forced to work in the production of wolframite, or tungsten ore, in some mines in the Democratic Republic of the Congo. Based on estimates from NGOs and the U.S. Department of State, hundreds of children are working in conditions of forced labor in the mines in Eastern Congo, particularly in North and South Kivu. Some children are forced to work at the mines with their families in situations of bonded labor, while other children are sent away to the mines by their parents to pay off the family's debt. These children are paid little, if at all. In addition, many mines are controlled by military officers or armed groups, which are known to round up villagers, including children, at gunpoint and force them to work with threats of violence. These forcibly-recruited children do not have freedom of movement and do not receive payment for their work. |
Child Labor, Forced Labor |
| China | There are reports that children, mostly ages 13-16, are forced to produce toys in China. The most recently available data from an NGO study indicates that hundreds of children are exploited in this manner. Reports indicate children from Sichuan, Guangxi, and other provinces are sent to work primarily in Guangdong to make toys. Some of these children are trafficked after being recruited through deceptive promises, and others are forced to work by teachers through work-study programs. Children of the Yi ethnic minority in Liangshan prefecture of Sichuan are particularly vulnerable. The children report being forced to work long hours under threat of financial penalty and being fined for any mistakes in their work. Some children state that teachers withhold wages for “tuition” and management fees. In addition, employers withhold wages for months to prevent children from leaving. |
Child Labor, Forced Labor |
| Mexico | There are reports that men and women are forced to work in the production of tomatoes in Mexico. According to media reports, NGOs, and the U.S. Department of State, there are hundreds of forced labor victims working to produce tomatoes. Many of these victims report being recruited by middlemen, called enganchadores, that lie to workers about the nature and conditions of the work, wages, hours, and quality of living conditions. Sources report that cases of forced labor occur on both commercial tomato plantations and smallholder farms, and have been found in states such as Baja California, Coahuila, Jalisco, San Luis Potosi, and Sinaloa. According to available reports, indigenous farmworkers from impoverished regions of central and southern Mexico are particularly vulnerable to forced labor in the agricultural sector due to low education levels, linguistic barriers, and discrimination. Once on the farms, some men and women work up to 15 hours per day under the threat of dismissal and receive subminimum wage payments. There are reports of some workers being threatened with physical violence or physically abused for leaving their jobs. Workers also report finding themselves in overcrowded and unsanitary housing facilities with no access to potable water, latrines, electricity, and medical care. Some workers face growing indebtedness to company stores that often inflate the prices of their goods, forcing workers to purchase provisions on credit and limiting their ability to leave the farms. |
Child Labor, Forced Labor |
| China | There are reports that adults are forced to produce tomato products in China. Xinjiang is a major producer of tomato products, especially tomato paste. Victim testimonies, news media, and think tanks report that factories, including for tomato products, frequently engage in coercive recruitment; limit workers’ freedom of movement and communication; and subject workers to constant surveillance, retribution for religious beliefs, exclusion from community and social life, and isolation. More broadly, according to varied estimates, at least 100,000 to hundreds of thousands of Uyghurs, ethnic Kazakhs, and other Muslim minorities are being subjected to forced labor in China following detention in re-education camps. In addition to this, poor workers in rural areas may also experience coercion without detention. |
Forced Labor |
| Malawi | There are reports that children in Malawi are forced to work producing tobacco. Tobacco estates are concentrated in the Mzimba, Kasungu, Mchinji and Mzimba districts. According to the most recently available data from the ILO and NGOs, over 70,000 children work on tobacco plantations, some of them under conditions of bonded labor. Families working on tobacco estates sometimes become bonded to their landlords, and their children are forced to work to repay their family debts. Landlords charge these tenant workers for costs such as rent, fertilizer, and seeds; these costs often exceed the profit earned from the tobacco harvest and result in debt for the worker and his or her family. Some children are also hired under deceptive terms of work and promised payment, and then are paid little, if at all, at the end of the season. Some children are forced to work long hours, including overtime, and are forced to perform dangerous tasks, such as carrying heavy loads and using pesticides. In addition, certain children work under threats and penalties including physical, verbal, and sexual abuse, and do not receive food or pay. |
Child Labor, Forced Labor |
| Congo, Democratic Republic of the (DRC) | There are reports that children ages 5-17 are forced to work in the production of cassiterite, or tin ore, in some mines in the Democratic Republic of the Congo. Reports from NGOs and the U.S. Department of State indicate that many children have been identified working in conditions of forced labor in the mines in Eastern Congo, particularly in North and South Kivu. Some children are forced to work at the mines with their families in situations of bonded labor, while other children are sent away to the mines by their parents to pay off the family's debt. These children are paid little, if at all. In addition, many mines are controlled by military officers or armed groups, which are known to round up villagers, including children, at gunpoint and force them to work with threats of violence. These forcibly-recruited children do not have freedom of movement and do not receive payment for their work. |
Child Labor, Forced Labor |
| Brazil | Forced Labor | |
| Korea, North | Forced Labor | |
| Peru | Forced Labor |
your hand? Download ILAB's Sweat & Toil App today!
Are you a company looking to fight child labor and forced labor in supply
chains?