List of Goods Produced by Child Labor or Forced Labor
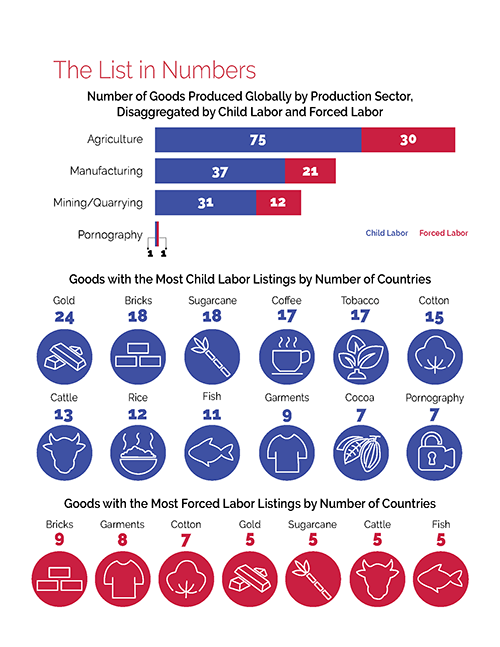
The Bureau of International Labor Affairs (ILAB) maintains a list of goods and their source countries which it has reason to believe are produced by child labor or forced labor in violation of international standards, as required under the Trafficking Victims Protection Reauthorization Act (TVPRA) of 2005 and subsequent reauthorizations. The List of Goods Produced by Child Labor or Forced Labor comprises 159 goods from 78 countries and areas, as of September 28, 2022.
ILAB maintains the List primarily to raise public awareness about forced labor and child labor around the world and to promote efforts to combat them; it is not intended to be punitive, but rather to serve as a catalyst for more strategic and focused coordination and collaboration among those working to address these problems.
Publication of the List has resulted in new opportunities for ILAB to engage with foreign governments to combat forced labor and child labor. It is also a valuable resource for researchers, advocacy organizations and companies wishing to carry out risk assessments and engage in due diligence on labor rights in their supply chains.
The countries on the List span every region of the world. The most common agricultural goods listed are sugarcane, cotton, coffee, tobacco, cattle, rice, and fish. In the manufacturing sector, bricks, garments, textiles, footwear, carpets, and fireworks appear most frequently. In mined or quarried goods, gold, coal and diamonds are most common.
ILAB published the initial TVPRA List in 2009 and updated it annually through 2014, following a set of procedural guidelines that were the product of an intensive public consultation process. ILAB now updates and publishes the List every other year, pursuant to changes in the law.
Procedural Guidelines
On January 25, 2024, ILAB's Office of Child Labor, Forced Labor, and Human Trafficking published Procedural Guidelines for the development and maintenance of the List of Goods from countries produced by child labor or forced labor in violation of international standards.
| Country/Area | Good Sort ascending | Exploitation Type |
|---|---|---|
| Ghana | There are reports that children ages 5-17 in Ghana are forced to work in the fishing industry, assisting primarily in the catching of tilapia, but also of such fish as mudfish, silverfish, catfish, latefish, and electric fish. According to the most recently available data from universities, NGOs, government raids, and international organizations, hundreds of children in the Lake Volta region have been rescued from the fishing industry, in which they were forced to undertake such tasks as diving to untangle fishing nets from underwater tree stumps. Children are often trafficked from the Volta, Central, Eastern, or Ashanti regions to Tato and other Lake Volta communities to work. Some of the children forced to work in the fishing industry are working in bonded labor after being sold or sent by their parents under a one- to three-year contract, for which the parents are promised payment on agreed-upon intervals. The children frequently are paid little, if at all, and are forced to work long hours. The children forced to work in the fishing industry often live with their employers, where they face physical violence and are not provided with sufficient food. |
Child Labor, Forced Labor |
| China | Reports indicate that more than 2,000 adult Uyghur and ethnic Kazakh workers have been involuntarily transferred out of Xinjiang to yarn factories in the east and forced to produce thread/yarn products. It also is likely that many others are subjected to forced labor at yarn factories within Xinjiang, particularly for cotton yarns. Victim testimonies, news media, and think tanks report that factories, including for thread/yarn, frequently engage in coercive recruitment; limit workers’ freedom of movement and communication; and subject workers to constant surveillance, retribution for religious beliefs, exclusion from community and social life, and threaten family members. Further, workers may undergo re-education to eradicate “extremism.” More broadly, according to varied estimates, at least 100,000 to hundreds of thousands of Uyghurs, ethnic Kazakhs, and other Muslim minorities are being subjected to forced labor in China following detention in re-education camps. In addition to this, poor workers in rural areas may also experience coercion without detention. Workers can be placed at factories within the Xinjiang Uyghur Autonomous Region, where the camps are located, or be transferred out of Xinjiang to factories in eastern China. |
Forced Labor |
| India | There are reports that forced labor conditions are prevalent among workers in the thread and yarn sector in India. In particular, workers in spinning mills in the state of Tamil Nadu are often recruited using deception about working conditions and wages. Sources indicate conditions of excessive and involuntary overtime, debt bondage, withholding of identity records, and restrictions on free movement of workers. |
Child Labor, Forced Labor |
| Ethiopia | There are reports that children, mostly boys as young as seven years old, produce woven textiles under conditions of forced labor in Ethiopia. These children typically work in Addis Ababa, however many come from the south, including Gamo Gofa and Wolaita zones, some of them as victims of trafficking. The trafficked children are often sold to recruiters, and the parents and children are deceived with false promises about the wages and opportunities for education while working. Some of the children sleep at the worksites, held in captivity and isolation, and are not provided with sufficient food. They are punished with physical abuse. Some children are forced to work long hours and overtime, and receive little, if any, pay. |
Child Labor, Forced Labor |
| Bangladesh | Child Labor | |
| Cambodia | Child Labor | |
| China | According to think tank and media reports, the textile industry works with the Government of China to make use of adult ethnic minority groups for forced, exploitative labor. Researchers note that Xinjiang is undergoing an expansion of the textile industry, and it is possible that hundreds of thousands of workers are being subjected to forced labor as part of this effort. Victim testimonies, news media, and think tanks report that factories, including for textiles, frequently engage in coercive recruitment; limit workers’ freedom of movement and communication; and subject workers to constant surveillance, retribution for religious beliefs, exclusion from community and social life, and threaten family members. Further, some workers have been subject to military-style management, government indoctrination, and are paid below the minimum wage. There are reports that adults are forced to produce textiles in China. More broadly, according to varied estimates, at least 100,000 to hundreds of thousands of Uyghurs, ethnic Kazakhs, and other Muslim minorities are being subjected to forced labor in China following detention in re-education camps. In addition to this, poor workers in rural areas may also experience coercion without detention. Workers can be placed at factories within the Xinjiang Uyghur Autonomous Region, where the camps are located, or be transferred out of Xinjiang to factories in eastern China. |
Child Labor, Forced Labor |
| Ghana | There is evidence that children ages 5 to 14 are involved in the weaving of textiles in Ghana. Based on an analysis of the Ghana Living Standards Survey, an estimated 23,856 child laborers are involved in the weaving of textiles. There are numerous health and safety issues associated with the textile industry. These hazards include chemical exposure from the processing and dyeing of materials, exposure to cotton and other organic dusts, musculoskeletal stresses, and noise exposure. The release of this survey demonstrates the Government of Ghana’s commitment to addressing child labor and its acknowledgement that data collection is vital to the design and implementation of sound policies and programs. |
Child Labor |
| Korea, North | Forced Labor | |
| Pakistan | There is evidence that children under 14 work in the production of textiles in Pakistan. Based on an analysis of the Pakistan Labour Force Survey 2017– 2018, an estimated 45,699 children are involved in child labor in the production of textiles. The release of this survey demonstrates the Government of Pakistan’s commitment to addressing child labor and its acknowledgment that data collection is vital to the design and implementation of sound policies and programs. |
Child Labor |
your hand? Download ILAB's Sweat & Toil App today!
Are you a company looking to fight child labor and forced labor in supply
chains?