List of Goods Produced by Child Labor or Forced Labor
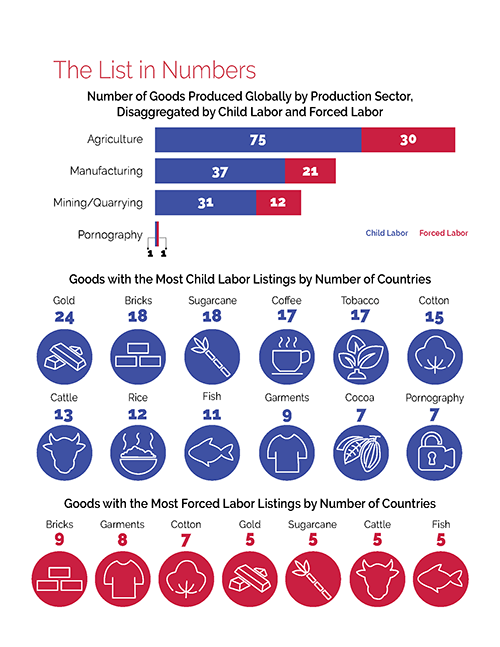
The Bureau of International Labor Affairs (ILAB) maintains a list of goods and their source countries which it has reason to believe are produced by child labor or forced labor in violation of international standards, as required under the Trafficking Victims Protection Reauthorization Act (TVPRA) of 2005 and subsequent reauthorizations. The List of Goods Produced by Child Labor or Forced Labor comprises 159 goods from 78 countries and areas, as of September 28, 2022.
ILAB maintains the List primarily to raise public awareness about forced labor and child labor around the world and to promote efforts to combat them; it is not intended to be punitive, but rather to serve as a catalyst for more strategic and focused coordination and collaboration among those working to address these problems.
Publication of the List has resulted in new opportunities for ILAB to engage with foreign governments to combat forced labor and child labor. It is also a valuable resource for researchers, advocacy organizations and companies wishing to carry out risk assessments and engage in due diligence on labor rights in their supply chains.
The countries on the List span every region of the world. The most common agricultural goods listed are sugarcane, cotton, coffee, tobacco, cattle, rice, and fish. In the manufacturing sector, bricks, garments, textiles, footwear, carpets, and fireworks appear most frequently. In mined or quarried goods, gold, coal and diamonds are most common.
ILAB published the initial TVPRA List in 2009 and updated it annually through 2014, following a set of procedural guidelines that were the product of an intensive public consultation process. ILAB now updates and publishes the List every other year, pursuant to changes in the law.
Procedural Guidelines
On January 25, 2024, ILAB's Office of Child Labor, Forced Labor, and Human Trafficking published Procedural Guidelines for the development and maintenance of the List of Goods from countries produced by child labor or forced labor in violation of international standards.
| Country/Area Sort descending | Good | Exploitation Type |
|---|---|---|
| El Salvador | There is evidence that children ages 5 to 17 are engaged in the production of baked goods in El Salvador. According to the Government of El Salvador’s Multi-Purpose Household Survey of 2015, a working child is considered to be engaged in hazardous child labor if the child is performing work that is hazardous according to national legislation. The survey estimates that 123,259 children ages 5 to 17 perform hazardous child labor in El Salvador, including using dangerous tools, carrying heavy loads, working with chemicals, working long or night shifts, and being exposed to dust, smoke, or extreme heat or humidity. Approximately 9,737 of these children in hazardous child labor are engaged in the production of baked goods. The release of this survey demonstrates the Government of El Salvador’s commitment to addressing child labor and its acknowledgement that data collection is vital to the design and implementation of sound policies and programs. |
Child Labor |
| El Salvador | Child Labor | |
| El Salvador | There is evidence that children ages 5 to 17 are engaged in cattle raising in El Salvador. According to the Government of El Salvador’s Multi-Purpose Household Survey of 2015, a working child is considered to be engaged in hazardous child labor if the child is performing work that is hazardous according to national legislation. The survey estimates that 123,259 children ages 5 to 17 perform hazardous child labor in El Salvador, including using dangerous tools, carrying heavy loads, working with chemicals, working long or night shifts, and being exposed to dust, smoke, or extreme heat or humidity. Approximately 3,698 of these children in hazardous child labor are engaged in cattle raising. The release of this survey demonstrates the Government of El Salvador’s commitment to addressing child labor and its acknowledgement that data collection is vital to the design and implementation of sound policies and programs. |
Child Labor |
| El Salvador | Child Labor | |
| Eswatini | There is evidence that children ages 8 to 17 raise bovines in Eswatini. Child labor in this sector is concentrated in the rural areas of Hhohho, Lubombo, Manzini, and Shiselweni. In 2018, the Government of Eswatini and the International Labor Organization published results from the 2014 Survey on Child Labor in Herding in Rural Areas in Eswatini. According to international standards on the minimum age for work, children working below the age of 15 are engaged in child labor. The survey estimates that 72,332 children below the age of 15 raise bovines. Children perform physically arduous tasks while herding in the grasslands and mountainous regions, and risk occupational injury and disease from exposure to dangerous tools, insecticides and herbicides. Children’s injuries include fractures, dislocations and sprains, burns, frostbite, breathing problems, skin problems, extreme fatigue, and snake bites. The release of this survey demonstrates the Government of Eswatini’s commitment to addressing child labor and its acknowledgement that data collection is vital to the design and implementation of sound policies and programs. |
Child Labor |
| Ethiopia | Child Labor | |
| Ethiopia | There are reports that children ages 8 to 17 produce khat in Ethiopia. According to a study from 2017, between 50 percent and 70 percent of khat workers in Wondo Genet’s Chuko town and Aweday, in Eastern Hararge, are children. Sources estimate that 5,000 children in Aweday are connected to the industry, approximately 2,000 of whom are under age 15. Although khat (Catha edulis) is legal in Ethiopia, the plant releases two highly addictive central nervous system stimulants – cathinone and cathine – whose acute and long-term neurological effects include khat-induced psychosis. Children involved in khat cultivation, pruning, and bundling may become addicted to the drug due to contact with excretions from the plant. Moreover, child laborers are unable to attend school and they work long nights. |
Child Labor |
| Ethiopia | There are reports that children, mostly boys as young as seven years old, produce woven textiles under conditions of forced labor in Ethiopia. These children typically work in Addis Ababa, however many come from the south, including Gamo Gofa and Wolaita zones, some of them as victims of trafficking. The trafficked children are often sold to recruiters, and the parents and children are deceived with false promises about the wages and opportunities for education while working. Some of the children sleep at the worksites, held in captivity and isolation, and are not provided with sufficient food. They are punished with physical abuse. Some children are forced to work long hours and overtime, and receive little, if any, pay. |
Child Labor, Forced Labor |
| Ethiopia | Child Labor | |
| Ghana | Child Labor |
your hand? Download ILAB's Sweat & Toil App today!
Are you a company looking to fight child labor and forced labor in supply
chains?