List of Goods Produced by Child Labor or Forced Labor
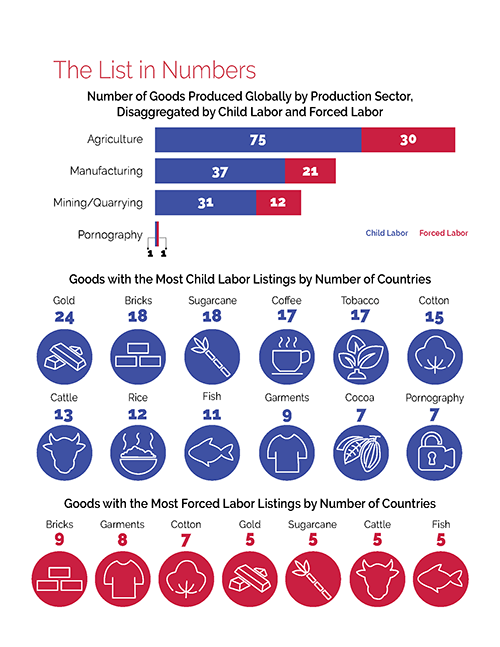
The Bureau of International Labor Affairs (ILAB) maintains a list of goods and their source countries which it has reason to believe are produced by child labor or forced labor in violation of international standards, as required under the Trafficking Victims Protection Reauthorization Act (TVPRA) of 2005 and subsequent reauthorizations. The List of Goods Produced by Child Labor or Forced Labor comprises 159 goods from 78 countries and areas, as of September 28, 2022.
ILAB maintains the List primarily to raise public awareness about forced labor and child labor around the world and to promote efforts to combat them; it is not intended to be punitive, but rather to serve as a catalyst for more strategic and focused coordination and collaboration among those working to address these problems.
Publication of the List has resulted in new opportunities for ILAB to engage with foreign governments to combat forced labor and child labor. It is also a valuable resource for researchers, advocacy organizations and companies wishing to carry out risk assessments and engage in due diligence on labor rights in their supply chains.
The countries on the List span every region of the world. The most common agricultural goods listed are sugarcane, cotton, coffee, tobacco, cattle, rice, and fish. In the manufacturing sector, bricks, garments, textiles, footwear, carpets, and fireworks appear most frequently. In mined or quarried goods, gold, coal and diamonds are most common.
ILAB published the initial TVPRA List in 2009 and updated it annually through 2014, following a set of procedural guidelines that were the product of an intensive public consultation process. ILAB now updates and publishes the List every other year, pursuant to changes in the law.
Procedural Guidelines
On January 25, 2024, ILAB's Office of Child Labor, Forced Labor, and Human Trafficking published Procedural Guidelines for the development and maintenance of the List of Goods from countries produced by child labor or forced labor in violation of international standards.
| Country/Area Sort descending | Good | Exploitation Type |
|---|---|---|
| Cambodia | There are reports that children are forced to produce bricks in Cambodia. According to international researchers and NGOs, numerous incidents of forced child labor have been reported in Cambodia. Reports estimate over 9.3 percent of brick workers are children. However, with upwards of tens of thousands of workers employed at brick kilns and the casual nature of work in brick kilns, this number is likely higher. A cycle of multi-generational debt bondage is created when adults are unable to pay back the high interest charged on loans offered by brick kiln owners and are forced to pass along outstanding debts to their children. Children either inherit or are born into debt bondage and are threatened with arrest or are forced to pay additional debt if they try to leave the brick kiln without repaying their debts in full. |
Child Labor, Forced Labor |
| Cambodia | Child Labor | |
| Cambodia | Child Labor | |
| Cameroon | Child Labor | |
| Cameroon | There are reports that children are involved in the mining of gold in eastern Cameroon. Children often mine alongside their families in artisanal mines, and reports indicate that their ages range from under age 10 to 17. Sometimes children mine gold by themselves for sale on the black market. Evidence of child labor has been found in Batouri and Kambele, near the border with the Central African Republic. Reports indicate that thousands of children in Kambele work in artisanal gold mining, while in nearby Batouri, roughly 90 percent of children participate in gold mining. Children mine in hazardous conditions, including standing in stagnant water, working underground, and using mercury to extract the gold dust. Many children leave school to work in gold mining, and a report indicates that over 75 percent of the students in one school stopped attending school to mine gold. |
Child Labor |
| Central African Republic | Child Labor | |
| Chad | Child Labor | |
| China | ILAB has reason to believe that multiple solar products produced in China are made with an input using forced labor, specifically from polysilicon produced in China. These products include photovoltaic ingots and wafers (China), solar cells (China), and solar modules (China). Polysilicon was added to ILAB’s List of Goods Produced by Child Labor or Forced Labor in 2021 for forced labor. Forty-five percent of the world’s solar-grade polysilicon and more than half of China’s polysilicon is produced in the Xinjiang Uyghur Autonomous Region, where research has shown it is produced under conditions of forced labor. China has 98 percent of the world's manufacturing capacity for photovoltaic ingots; 97 percent for photovoltaic wafers; 81 percent for solar cells; and 77 percent for solar modules, all of which are made with polysilicon. Many of the largest global producers of photovoltaic ingots and wafers, solar cells, and solar modules directly source polysilicon from entities believed to use forced labor in its production. In 2020, solar cells and modules imported from China accounted for over $24 billion. While the U.S. directly imported about 5 percent of its solar cells and modules from China, it is likely that additional solar cells and modules made with polysilicon produced with forced labor enter the U.S. through other countries. Many solar companies operating around the world have suppliers based in China and many are owned by Chinese companies. Over 42 percent of global imports of solar cells and modules come from China. This research suggests that other downstream products of polysilicon, such as semiconductors, silica-based goods, and solar generators, may be produced with an input produced with forced labor. |
Inputs Produced with Forced Labor |
| China | There are reports that adults are forced to work in the production of fish on China’s distant-water fishing fleet. China’s fleet is the largest in the world, with an estimated 3,000 fishing vessels, and contains a wide variety of vessels, from longliners to purse seiners, operating on the high seas and in foreign countries’ exclusive economic zones in every region of the world. The majority of the crew on board are migrant workers from Indonesia and the Philippines, who are particularly vulnerable to forced labor. It is estimated that there are tens of thousands of workers who are sometimes recruited by agencies that deceive workers with false information regarding their wages and the terms of the contracts, and require the workers to pay recruitment fees and sign debt contracts. According to various sources, numerous incidents of forced labor have been reported on Chinese fishing vessels. While on board the vessels, workers’ identity documents are often confiscated, the crew spends months at sea without stopping at a port of call, and they are forced to work 18 to 22 hours a day with little rest. Workers face hunger and dehydration, live in degrading and unhygienic conditions, are subjected to physical violence and verbal abuse, are prevented from leaving the vessel or ending their contracts, and are frequently not paid their promised wages. |
Forced Labor |
| China | Forced Labor |
your hand? Download ILAB's Sweat & Toil App today!
Are you a company looking to fight child labor and forced labor in supply
chains?