List of Goods Produced by Child Labor or Forced Labor
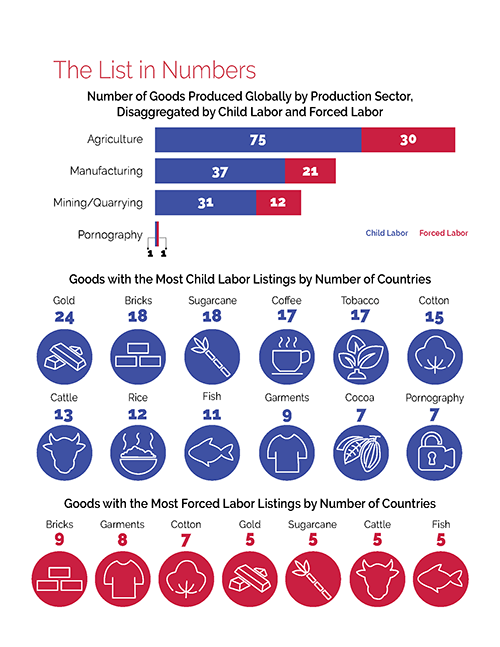
The Bureau of International Labor Affairs (ILAB) maintains a list of goods and their source countries which it has reason to believe are produced by child labor or forced labor in violation of international standards, as required under the Trafficking Victims Protection Reauthorization Act (TVPRA) of 2005 and subsequent reauthorizations. The List of Goods Produced by Child Labor or Forced Labor comprises 159 goods from 78 countries and areas, as of September 28, 2022.
ILAB maintains the List primarily to raise public awareness about forced labor and child labor around the world and to promote efforts to combat them; it is not intended to be punitive, but rather to serve as a catalyst for more strategic and focused coordination and collaboration among those working to address these problems.
Publication of the List has resulted in new opportunities for ILAB to engage with foreign governments to combat forced labor and child labor. It is also a valuable resource for researchers, advocacy organizations and companies wishing to carry out risk assessments and engage in due diligence on labor rights in their supply chains.
The countries on the List span every region of the world. The most common agricultural goods listed are sugarcane, cotton, coffee, tobacco, cattle, rice, and fish. In the manufacturing sector, bricks, garments, textiles, footwear, carpets, and fireworks appear most frequently. In mined or quarried goods, gold, coal and diamonds are most common.
ILAB published the initial TVPRA List in 2009 and updated it annually through 2014, following a set of procedural guidelines that were the product of an intensive public consultation process. ILAB now updates and publishes the List every other year, pursuant to changes in the law.
Procedural Guidelines
On January 25, 2024, ILAB's Office of Child Labor, Forced Labor, and Human Trafficking published Procedural Guidelines for the development and maintenance of the List of Goods from countries produced by child labor or forced labor in violation of international standards.
| Country/Area Sort descending | Good | Exploitation Type |
|---|---|---|
| China | There are reports that children ages 13-15 are forced to produce electronics in China. Based on the most recently available data from media sources, government raids, and NGOs, hundreds of cases of forced child labor have been reported in factories in Guangdong province, but the children are often from Henan, Shanxi, or Sichuan provinces. In some cases, children are forced to work in electronics factories through arrangements between the factories and the schools that the children attend in order to cover alleged tuition debts. The forced labor programs are described as student apprenticeships; however, the children report that they were forced to remain on the job and not allowed to return home. Half of the students' wages are sent directly to the schools, and the children receive little compensation after deductions are made for food and accommodations. In other cases, children are abducted or deceived by recruiters, sent to Guangdong, and sold to employers. Some children are held captive, forced to work long hours for little pay. |
Child Labor, Forced Labor |
| Colombia | There are reports that children in Colombia as young as 11 years old are forced to cultivate and pick coca, and to scrape coca leaves. The Government, NGOs, media, and the ILO indicate that some children are forcibly recruited by non-state armed groups, such as the Revolutionary Armed Forces of Colombia, the National Liberation Army, and criminal groups to pick coca. Others are forced by drug traffickers. Criminal and illegal armed groups use threats of torture or death to prevent children from attempting to escape. |
Child Labor, Forced Labor |
| Congo, Democratic Republic of the (DRC) | There are reports that children ages 5-17 are forced to work in the production of wolframite, or tungsten ore, in some mines in the Democratic Republic of the Congo. Based on estimates from NGOs and the U.S. Department of State, hundreds of children are working in conditions of forced labor in the mines in Eastern Congo, particularly in North and South Kivu. Some children are forced to work at the mines with their families in situations of bonded labor, while other children are sent away to the mines by their parents to pay off the family's debt. These children are paid little, if at all. In addition, many mines are controlled by military officers or armed groups, which are known to round up villagers, including children, at gunpoint and force them to work with threats of violence. These forcibly-recruited children do not have freedom of movement and do not receive payment for their work. |
Child Labor, Forced Labor |
| Congo, Democratic Republic of the (DRC) | There are reports that children ages 10-16 are forced to work in the production of gold in some mines in the Democratic Republic of the Congo. Based on the most recently available NGO evidence, thousands of children are working in conditions of forced labor in the mines in Eastern Congo, particularly in North and South Kivu. Some children are forced to work at the mines with their families in situations of bonded labor, while other children are sent away to the mines by their parents to pay off the family's debt. Child miners are paid little if at all. Many mines are controlled by military officers or armed groups which force children to work. Some children are abducted to work in the mines. |
Child Labor, Forced Labor |
| Congo, Democratic Republic of the (DRC) | There are reports that children ages 5-17 are forced to work in the production of coltan, or tantalum ore, in some mines in the Democratic Republic of the Congo. Reports from the U.S. Department of State and NGOs state that many children have been identified working in conditions of forced labor in the mines in Eastern Congo, particularly in North and South Kivu. Some children are forced to work at the mines with their families in situations of bonded labor, while other children are sent away to the mines by their parents to pay off the family's debt. These children are paid little, if at all. In addition, many mines are controlled by military officers or armed groups, which are known to round up villagers, including children, at gunpoint and force them to work with threats of violence. These forcibly-recruited children do not have freedom of movement and do not receive payment for their work. |
Child Labor, Forced Labor |
| Congo, Democratic Republic of the (DRC) | There are reports that children ages 5-17 are forced to work in the production of cassiterite, or tin ore, in some mines in the Democratic Republic of the Congo. Reports from NGOs and the U.S. Department of State indicate that many children have been identified working in conditions of forced labor in the mines in Eastern Congo, particularly in North and South Kivu. Some children are forced to work at the mines with their families in situations of bonded labor, while other children are sent away to the mines by their parents to pay off the family's debt. These children are paid little, if at all. In addition, many mines are controlled by military officers or armed groups, which are known to round up villagers, including children, at gunpoint and force them to work with threats of violence. These forcibly-recruited children do not have freedom of movement and do not receive payment for their work. |
Child Labor, Forced Labor |
| Côte d'Ivoire | There are reports that children from within Côte d'Ivoire, as well as migrant children from Benin, Burkina Faso, Guinea, Mali, Nigeria, and Togo, are working under conditions of forced labor on Ivoirian cocoa farms. Based on the most recently available estimate from Tulane University, over 4,000 children work in conditions of forced labor in the production of cocoa in Côte d'Ivoire. Some children are sold by their parents to traffickers, some are kidnapped, and others migrate willingly but fall victim to traffickers who sell them to recruiters or farmers, where they end up in conditions of bonded labor. Some farmers buy the children and refuse to let them leave the farm until the debt of their purchase has been worked off. The children are frequently not paid for their work; some of their wages are paid to the recruiter or trafficker. These children are held against their will on isolated farms, are locked in their living quarters at night, and are threatened and beaten if they attempt to escape. They are punished by their employers with physical abuse. They are forced to work long hours, including overtime, and are required to work even when they are sick. Some children are denied sufficient food by their traffickers and employers. Some children are forced to perform dangerous tasks, including carrying heavy loads, using machetes and sharp tools, and applying pesticides and fertilizers. |
Child Labor, Forced Labor |
| Côte d'Ivoire | There are reports that children ages 14-17 and younger in Côte d'Ivoire are forced to work on coffee plantations. Based on a research study, thousands of children are involved in this type of labor. Some children are forcibly recruited, or recruited through deceptive means, and transported to coffee plantations in Côte d'Ivoire from nearby countries including Benin, Mali, Togo, and Burkina Faso. These children are sold to traffickers. Other children leave their home countries or communities voluntarily, but end up in situations where they are not paid and have no means to return home. Some children are forced to work for three or four years before receiving payment or returning home. Others are forced to work, even if sick, and prevented from leaving the plantations through threat of physical violence, withheld payments, or denial of food. |
Child Labor, Forced Labor |
| Dominican Republic | There are reports that adults are forced to work in the harvesting and production of sugarcane in the Dominican Republic. These adults, the majority of whom are undocumented or stateless, are predominantly of Haitian origin or descent. Reports from civil society organizations, news media, worker interviews, field research, and other sources indicate the existence of the following forced labor indicators in the sugarcane sector: withholding of wages, abusive working and living conditions, excessive overtime, isolation and restriction of movement, and deceptive recruitment practices. For some workers, a precarious legal status and lack of identity documents limit their movement and have led to isolation and fears of reprisal, denouncement to authorities, loss of company-provided housing and deportation for complaining about unlawful labor conditions. In addition, illiteracy, low levels of education, and language barriers can impede their understanding and exercising of labor rights, thus increasing their vulnerability to labor exploitation. |
Child Labor, Forced Labor |
| Ethiopia | There are reports that children, mostly boys as young as seven years old, produce woven textiles under conditions of forced labor in Ethiopia. These children typically work in Addis Ababa, however many come from the south, including Gamo Gofa and Wolaita zones, some of them as victims of trafficking. The trafficked children are often sold to recruiters, and the parents and children are deceived with false promises about the wages and opportunities for education while working. Some of the children sleep at the worksites, held in captivity and isolation, and are not provided with sufficient food. They are punished with physical abuse. Some children are forced to work long hours and overtime, and receive little, if any, pay. |
Child Labor, Forced Labor |
your hand? Download ILAB's Sweat & Toil App today!
Are you a company looking to fight child labor and forced labor in supply
chains?