List of Goods Produced by Child Labor or Forced Labor
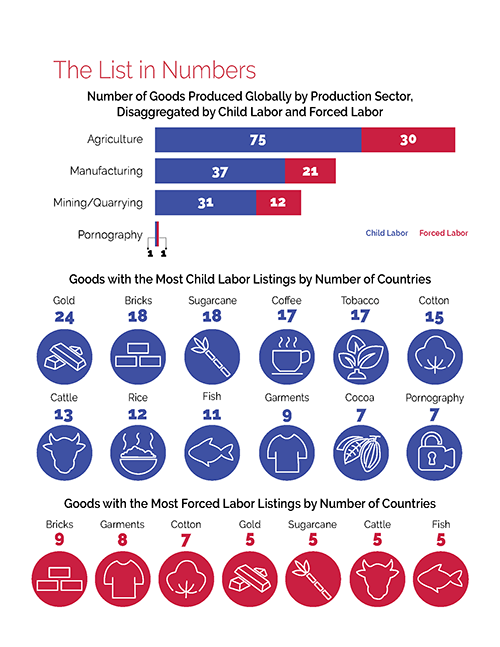
The Bureau of International Labor Affairs (ILAB) maintains a list of goods and their source countries which it has reason to believe are produced by child labor or forced labor in violation of international standards, as required under the Trafficking Victims Protection Reauthorization Act (TVPRA) of 2005 and subsequent reauthorizations. The List of Goods Produced by Child Labor or Forced Labor comprises 159 goods from 78 countries and areas, as of September 28, 2022.
ILAB maintains the List primarily to raise public awareness about forced labor and child labor around the world and to promote efforts to combat them; it is not intended to be punitive, but rather to serve as a catalyst for more strategic and focused coordination and collaboration among those working to address these problems.
Publication of the List has resulted in new opportunities for ILAB to engage with foreign governments to combat forced labor and child labor. It is also a valuable resource for researchers, advocacy organizations and companies wishing to carry out risk assessments and engage in due diligence on labor rights in their supply chains.
The countries on the List span every region of the world. The most common agricultural goods listed are sugarcane, cotton, coffee, tobacco, cattle, rice, and fish. In the manufacturing sector, bricks, garments, textiles, footwear, carpets, and fireworks appear most frequently. In mined or quarried goods, gold, coal and diamonds are most common.
ILAB published the initial TVPRA List in 2009 and updated it annually through 2014, following a set of procedural guidelines that were the product of an intensive public consultation process. ILAB now updates and publishes the List every other year, pursuant to changes in the law.
Procedural Guidelines
On January 25, 2024, ILAB's Office of Child Labor, Forced Labor, and Human Trafficking published Procedural Guidelines for the development and maintenance of the List of Goods from countries produced by child labor or forced labor in violation of international standards.
| Country/Area Sort ascending | Good | Exploitation Type |
|---|---|---|
| Vietnam | There are reports of children ages 10-18 and some as young as 6 who work under conditions of forced labor producing garments in Vietnam. The most recently available information from government raids, NGOs and media reports indicates that groups of children are found in small privately-owned factories and informal workshops. These workplaces are located primarily in and around Ho Chi Minh City; however, many of these children have migrated, or have been trafficked, from the countryside and from central or northern provinces. Many of the children live in the factories; employers prevent the children from leaving through force and/or by withholding their wages. In some cases, employers pay the children only after a full year of work or at the completion of a multi-year contract. Employers refuse to pay the children who leave before the end of the contract; some withhold a portion of the wages dues under the contract in order to force the children to remain an additional year. The children are forced to work long hours, up to 18 hours per day, sometimes late into the night, and with few breaks. Reports indicate that these children are beaten or threatened with physical violence by their employers. In addition, there are reports of children as young as 12 years old found to be working while confined in government-run detention centers. These children are forced to sew garments under threat of physical or other punishments and without pay. |
Child Labor, Forced Labor |
| Venezuela | There are reports that adults are forced to work in the mining of gold in Venezuela. Research indicates that forced labor occurs throughout the Orinoco Mining Arc, a swath of land in Venezuela’s southern Bolivar state, where the majority of Venezuela’s gold is concentrated. It is estimated that there are between 300,000 and 500,000 gold miners in Venezuela. Mines are largely run by armed and violent criminal groups, and research shows evidence that officials from the Government of Venezuela, including members of security forces and local authorities, have colluded with and allowed members of non-state armed groups to commit human rights violations and labor abuses. Miners experience unsafe working conditions, unsafe and degrading living conditions, extortion and financial penalties, limited freedom of communication, and threats of violence and torture. |
Forced Labor |
| Uzbekistan | There are reports that adults are forced to cultivate silk cocoons in Uzbekistan. A silk cocoon is the protective casing a silkworm spins around itself before metamorphosing into a moth. Silk cocoons can be processed and unwound to produce silk thread. Forced labor in cocoon production predominantly occurs among farmers in the south of the country, although evidence suggests that other rural families are also subjected to forced labor in this sector. Based on estimates from the Uzbek-German Forum, a majority of the over 45,000 farmers in Uzbekistan who produce silk cocoons each year do not have the freedom to refuse this work; they are compelled to perform it by government officials. Regional- and district-level officials assign each farmer a quota for the production of silk cocoons, and threaten farmers with fines, the loss of their leased farmland, or physical violence if they fail to meet the quota. Farmers are required to sell their silk cocoons back to the government at an official procurement price, which can be too low to offset the cost of cultivating the cocoons, and often experience underpayment, delayed payment, or receive no payment at all. Regional- and district-level governments also impose quotas on neighborhood councils called mahallas, which use their authority over distribution of social benefit payments to force neighborhood residents to cultivate silk cocoons. Because silkworms require constant attention and the maintenance of a carefully controlled environment in order to survive, farmers and rural families often cultivate cocoons in several rooms of their own homes and many work more than 20 hours a day during the approximately month-long cultivation period. |
Forced Labor |
| Turkmenistan | Child Labor, Forced Labor | |
| Thailand | There are reports that children are forced to process shrimp in Thailand. Burmese and Cambodian immigrants are particularly vulnerable to forced child labor in the shrimp industry. A UN report identified approximately 150 children working, many alongside their mothers, in Klong Yai district near the Cambodia border. Children are often forced to peel and sort shrimp. Some are forced to work long hours without breaks, physically abused, and prohibited from leaving the worksite. They frequently have their identity documents confiscated by their employers. In some cases, child workers are paid little, if at all, and their wages are deducted to repay debts related to recruitment, food, and/or lodging. The children often endure these conditions under the threat of dismissal and arrest by immigration police.
|
Child Labor, Forced Labor |
| Thailand | Forced Labor | |
| Thailand | There are reports that mostly girls as young as 11 are forced to produce garments in Thailand. Migrant children from Laos and Burma are particularly vulnerable. The ILO, media, trade unions, government raids, and NGOs report forced child labor in garment factories in Bangkok and along the Burma border in Mae Sai and Mae Sot. Many children live at the worksite, and their freedom of movement is sometimes restricted through confiscation of identity documents and threats of arrest. Children are often forced to work long hours and overtime, and are paid little, if at all. Some are not provided sufficient food and are physically abused. Mistakes made during the course of work are sometimes penalized with wage deductions. |
Child Labor, Forced Labor |
| Tajikistan | There are reports that children ages 14-17 and some as young as 7 are forced to work during the annual cotton harvest in Tajikistan. Monitoring teams discover multiple cases of compulsory mobilization across several districts of the country each year. In these cases, school officials mobilize classes to work in the harvest and teachers supervise them in the fields. Some children receive threats regarding exams, grades, and even expulsion from school for refusal to work. The children are typically sent to the fields after class hours. Farmers negotiate directly with the schools to mobilize the students to work, and the schools may keep some or all of the children's wages. Some of the children are required to pick a quota of 66 pounds of cotton daily. |
Child Labor, Forced Labor |
| Taiwan | There are reports that adults are forced to work in the production of fish on Taiwan’s distant-water fishing fleet. Taiwan’s fleet is the second largest in the world, with more than 1,100 fishing vessels, comprising approximately 36 percent of the world’s tuna longliner fleet, and operating on the high seas and in the exclusive economic zones of more than 30 countries. An estimated 35,000 migrant workers are employed by the fleet. The majority of these workers are recruited overseas, mostly from Indonesia and the Philippines, by agencies that sometimes deceive workers with false information regarding their wages and the terms of the contracts, and require the workers to pay recruitment fees and sign debt contracts. According to various sources, numerous incidents of forced labor have been reported on Taiwan-flagged fishing vessels. While on board the vessels, workers’ identity documents are often confiscated, and the crew spends months at sea without stopping at a port of call, and they are forced to work 18 to 22 hours a day with little rest. Workers face hunger and dehydration, live in degrading and unhygienic conditions, are subjected to physical violence and verbal abuse, are prevented from leaving the vessel or ending their contracts, and are frequently not paid their promised wages or have food and lodging fees illegally deducted from their wages. |
Forced Labor |
| South Sudan | There are reports that children, especially boys, are abducted and forced to herd cattle in South Sudan. Hundreds of abductions have been reported, particularly in communities in Jonglei and Eastern Equatoria states. The children are abducted when rival tribes or ethnic groups enter communities to steal cattle, as well as during other inter-ethnic or inter-tribal disputes; some of these children are enslaved to herd cattle. |
Child Labor, Forced Labor |
your hand? Download ILAB's Sweat & Toil App today!
Are you a company looking to fight child labor and forced labor in supply
chains?