List of Goods Produced by Child Labor or Forced Labor
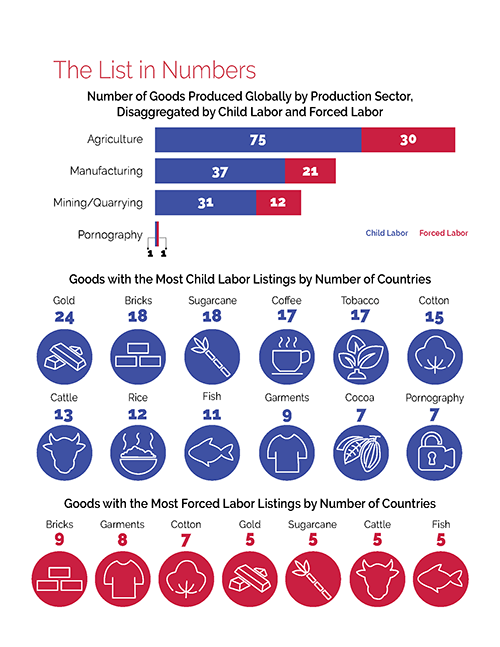
The Bureau of International Labor Affairs (ILAB) maintains a list of goods and their source countries which it has reason to believe are produced by child labor or forced labor in violation of international standards, as required under the Trafficking Victims Protection Reauthorization Act (TVPRA) of 2005 and subsequent reauthorizations. The List of Goods Produced by Child Labor or Forced Labor comprises 159 goods from 78 countries and areas, as of September 28, 2022.
ILAB maintains the List primarily to raise public awareness about forced labor and child labor around the world and to promote efforts to combat them; it is not intended to be punitive, but rather to serve as a catalyst for more strategic and focused coordination and collaboration among those working to address these problems.
Publication of the List has resulted in new opportunities for ILAB to engage with foreign governments to combat forced labor and child labor. It is also a valuable resource for researchers, advocacy organizations and companies wishing to carry out risk assessments and engage in due diligence on labor rights in their supply chains.
The countries on the List span every region of the world. The most common agricultural goods listed are sugarcane, cotton, coffee, tobacco, cattle, rice, and fish. In the manufacturing sector, bricks, garments, textiles, footwear, carpets, and fireworks appear most frequently. In mined or quarried goods, gold, coal and diamonds are most common.
ILAB published the initial TVPRA List in 2009 and updated it annually through 2014, following a set of procedural guidelines that were the product of an intensive public consultation process. ILAB now updates and publishes the List every other year, pursuant to changes in the law.
Procedural Guidelines
On January 25, 2024, ILAB's Office of Child Labor, Forced Labor, and Human Trafficking published Procedural Guidelines for the development and maintenance of the List of Goods from countries produced by child labor or forced labor in violation of international standards.
| Country/Area Sort descending | Good | Exploitation Type |
|---|---|---|
| Paraguay | There is evidence that children ages 5 to 17 grow sweet potatoes in Paraguay. In 2016, the Government of Paraguay published representative results from the Survey of Activities of Rural Area Children and Adolescents 2015. The survey considers a working child to be engaged in child labor if the child is below the minimum age for employment of 14 or the child is performing work that is hazardous according to national legislation. The survey estimates that 301,827 children ages 5 to 17 perform hazardous work in rural areas of Paraguay and indicates that children working in agriculture experience accidents and illnesses, including from using dangerous tools and handling chemicals. According to the survey, almost 13 percent of Paraguayan children engaged in child labor in agriculture do not attend school. The survey estimates that 8,143 child laborers grow sweet potatoes throughout rural areas in Paraguay. Approximately 4,912 of child laborers growing sweet potatoes are below the minimum age for employment in Paraguay. The survey indicates that more boys than girls are engaged in child labor producing sweet potatoes. The release of this survey demonstrates the Government of Paraguay’s commitment to addressing child labor and its acknowledgement that data collection is vital to the design and implementation of sound policies and programs. |
Child Labor |
| Paraguay | There is evidence that children ages 5 to 17 grow peppers in Paraguay. In 2016, the Government of Paraguay published representative results from the Survey of Activities of Rural Area Children and Adolescents 2015. The survey considers a working child to be engaged in child labor if the child is below the minimum age for employment of 14 or the child is performing work that is hazardous according to national legislation. The survey estimates that 301,827 children ages 5 to 17 perform hazardous work in rural areas of Paraguay and indicates that children working in agriculture experience accidents and illnesses, including from using dangerous tools and handling chemicals. According to the survey, almost 13 percent of Paraguayan children engaged in child labor in agriculture do not attend school. The survey estimates that 6,594 child laborers grow peppers throughout rural areas in Paraguay. The survey indicates that more boys than girls are engaged in child labor producing peppers. The release of this survey demonstrates the Government of Paraguay’s commitment to addressing child labor and its acknowledgement that data collection is vital to the design and implementation of sound policies and programs. |
Child Labor |
| Paraguay | There is evidence that children ages 5 to 17 raise goats in Paraguay. In 2016, the Government of Paraguay published results from the Survey of Activities of Rural Area Children and Adolescents 2015, a representative survey of children’s work in rural areas. The survey considers a working child to be engaged in child labor if the child is below the minimum age for employment of 14 or the child is performing work that is hazardous according to national legislation. The survey estimates that 301,827 children ages 5 to 17 perform hazardous work in rural areas of Paraguay and indicates that children working in agriculture experience accidents and illnesses, including from using dangerous tools and handling chemicals. According to the survey, almost 13 percent of Paraguayan children engaged in child labor in agriculture do not attend school. The survey estimates that 8,584 child laborers raise goats throughout rural areas in Paraguay. Approximately 4,714 child laborers raising goats are below the minimum age for employment in Paraguay. The survey indicates that more boys than girls are engaged in child labor in goat raising. The release of this survey demonstrates the Government of Paraguay’s commitment to addressing child labor and its acknowledgement that data collection is vital to the design and implementation of sound policies and programs. |
Child Labor |
| Paraguay | There is evidence that children ages 5 to 17 grow beans in Paraguay. In 2016, the Government of Paraguay published representative results from the Survey of Activities of Rural Area Children and Adolescents 2015. The survey considers a working child to be engaged in child labor if the child is below the minimum age for employment of 14 or is performing work that is hazardous according to national legislation. The survey estimates that 301,827 children ages 5 to 17 perform hazardous work in rural areas of Paraguay and indicates that children working in agriculture experience accidents and illnesses, including from using dangerous tools and handling chemicals. According to the survey, almost 13 percent of Paraguayan children engaged in child labor in agriculture do not attend school. The survey estimates that 71,839 child laborers grow poroto beans throughout rural areas in Paraguay. Approximately 31,372 of child laborers growing poroto beans are below the minimum age for employment in Paraguay. The survey indicates that child labor also occurs in the cultivation of other varieties of beans, including habilla, poroto manteca, and feijao, and that more boys than girls are engaged in child labor producing beans. The release of this survey demonstrates the Government of Paraguay’s commitment to addressing child labor and its acknowledgement that data collection is vital to the design and implementation of sound policies and programs. |
Child Labor |
| Paraguay | There is evidence that children ages 5 to 17 raise sheep in Paraguay. In 2016, the Government of Paraguay published representative results from the Survey of Activities of Rural Area Children and Adolescents 2015, a representative survey of children’s work in rural areas. The survey considers a working child to be engaged in child labor if the child is below the minimum age for employment of 14 or the child is performing work that is hazardous according to national legislation. The survey estimates that 301,827 children ages 5 to 17 perform hazardous work in rural areas of Paraguay and indicates that children working in agriculture experience accidents and illnesses, including from using dangerous tools and handling chemicals. According to the survey, almost 13 percent of Paraguayan children engaged in child labor in agriculture do not attend school. The survey estimates that 9,790 child laborers raise sheep throughout rural areas in Paraguay. Approximately 4,856 child laborers raising sheep are below the minimum age for employment in Paraguay. The survey indicates that more boys than girls are engaged in child labor in sheep raising. The release of this survey demonstrates the Government of Paraguay’s commitment to addressing child labor and its acknowledgement that data collection is vital to the design and implementation of sound policies and programs. |
Child Labor |
| Peru | Child Labor, Forced Labor | |
| Peru | Child Labor | |
| Peru | Forced Labor | |
| Peru | Child Labor | |
| Peru | Forced Labor |
your hand? Download ILAB's Sweat & Toil App today!
Are you a company looking to fight child labor and forced labor in supply
chains?