MEMORANDUM FOR REGIONAL ADMINISTRATORS
FROM: ALFRED B. ROBINSON, JR.
Acting Administrator
SUBJECT: Guidance on MSPA Vehicle Safety Standards
INTRODUCTION
The purpose of this memorandum is to provide guidance on vehicle terms and vehicle safety standards for the vehicle safety obligations found in the Migrant and Seasonal Agricultural Worker Act (MSPA) regulations in 29 CFR §§ 500. 100 to 500.128 (Subpart D).
Section 401 of the MSPA requires vehicles subject to the Act’s requirements to conform to standards prescribed by the Secretary and other applicable Federal and State safety standards when transporting migrant or seasonal workers. Subpart D of the MSPA regulations apply different vehicle safety standards to the transportation of MSPA workers depending on the vehicle type and how the vehicle is to be used. However, the different types of vehicles named in Subpart D are not defined.
The Wage and Hour Division (WHD) of the U.S. Department of Labor enforces vehicle safety standards found in 29 CFR § 500.104 (referred to as the DOL standards) and in 29 CFR § 500.105 (referred to as the DOT standards). The criteria for determining whether the standards in 29 CFR § 500.104 or the standards in 29 CFR § 500.105 apply can be found in 29 CFR § 500.102.
While terms used in the regulation should be given their ordinary meaning, the WHD recognizes the need to provide additional guidance to the field and to the regulated community. Thus, this memorandum provides specific definitions for the vehicle terms used in the regulations at Subpart D.
BACKGROUND
The MSPA vehicle safety requirements in 29 CFR § 500.105 were adopted from DOT regulations at 49 CFR § 398 titled “Transporting Migrant Workers.” 49 CFR § 398 does not define “passenger automobile or station wagon” but does provide a definition of a “bus” and a “truck.”
DOT regulations provide definitions for several vehicle types in 49 CFR § 571 Federal Motor Vehicle Safety Standards. These definitions are used by the National Highway Traffic Safety Administration (NHTSA) in their Federal Motor Vehicle Safety Standards (FMVSS) and the Federal Motor Carrier Safety Administration (FMSCA) makes reference to these definitions in their regulatory guidance for Federal Motor Carrier Safety Regulations (FMCSR). Additional definitions are also provided in 49 CFR § 523 Vehicle Classifications.
GUIDANCE ON VEHICLE TYPES
Subpart D of the MSPA regulations uses several specific vehicle terms as well as “passenger automobile or station wagon” and “any vehicle other than a passenger automobile or station wagon” to broadly distinguish vehicle types.
WHD will use the following descriptions of vehicle types when enforcing the motor vehicle safety standards in Subpart D.
The information below is largely based on DOT regulations and guidance. Adopting the same definitions used by US DOT agencies will provide consistency for the regulated community.
- Passenger automobile: a motor vehicle with motive power designed for carrying 10 persons or less (except a low-speed vehicle, a multipurpose passenger vehicle, a truck, a motorcycle, or a trailer). This includes a vehicle designated by the manufacturer as a station wagon.
- Bus: a motor vehicle with motive power, except a trailer, designed for carrying more than 10 persons.
- Multipurpose passenger vehicle: a motor vehicle with motive power, except a low-speed vehicle or trailer, designed to carry 10 persons or less which is constructed either on a truck chassis or with special features for occasional off-road operation (e.g. SUV). For MSPA enforcement purposes, a multipurpose passenger vehicle will be treated as a passenger automobile with the exception of those that meet the criteria of a truck (see below).
- Pickup truck: a truck (see below) whether extended cab, crew cab, etc. When transporting passengers only within the cab they will be treated as a station wagon as allowed in 29 CFR § 500.102(f).
- (1) Transport more than 10 persons;
- (2) Provide temporary living quarters;
- (3) Transport property on an open bed;
- (4) Provide greater cargo-carrying than passenger-carrying volume; or
- (5) Permit expanded use of the automobile for cargo-carrying purposes or other nonpassenger-carrying purposes through the removal of seats by means installed for that purpose by the automobile's manufacturer or with simple tools, such as screwdrivers and wrenches, so as to create a flat, floor level surface extending from the forward most point of installation of those seats to the rear of the automobile's interior.
- (1)
- (i) That has 4-wheel drive; or
- (ii) Is rated at more than 6,000 pounds gross vehicle weight; and
- (2) That has at least four of the following characteristics calculated when the automobile is at curb weight, on a level surface, with the front wheels parallel to the automobile's longitudinal centerline, and the tires inflated to the manufacturer's recommended pressure:
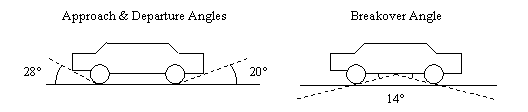
- (i) Approach angle of not less than 28 degrees (see diagram below);
- (ii) Breakover angle of not less than 14 degrees (see diagram below);
- (iii) Departure angle of not less than 20 degrees (see diagram below);
- (iv) Running clearance of not less than 20 centimeters;
- (v) Front and rear axle clearances of not less than 18 centimeters each.
- (See 49 CFR § 523.2 for further details.)
 |
|---|
A light truck designed to transport more than 10 passengers that meets all the passenger
compartment requirements in 29 CFR § 500.105(b)(3)(vi) and none of the other
characteristics above as a “truck” will be treated as a “bus.”
- Van: a light truck (see (a)(5) under truck above). A van with windows along both sides of the passenger-carrying area which is designed to carry 10 persons or less will be treated as a passenger automobile or when designed to carry more than 10 persons will be treated as a “bus” as long it meets all of the passenger compartment requirements in 29 CFR § 500.105(b)(3)(vi) and no other “truck” characteristics other than passenger capacity. A van designed for carrying cargo, typically without windows along both sides of the passenger-carrying area, is a truck. This regulation specifically prohibits the use of closed vans without windows or means to assure ventilation.
- Trailer: a motor vehicle with or without motive power, designed for carrying persons or property and for being drawn by another motor vehicle.
- Semi-trailer: a trailer so constructed that a substantial part of its weight rests upon or is carried by another motor vehicle.
Truck tractor: a truck designed primarily for drawing other motor vehicles and not so constructed
as to carry a load other than a part of the weight of the vehicle and the load so drawn.
- Low-speed vehicle: a 4-wheeled motor vehicle, other than a truck, whose speed attainable in 1.6 km (1 mile) is more than 32 kilometers per hour (20 miles per hour) and not more than 40 kilometers per hour (25 miles per hour) on a paved level surface.
“Designed” as used in this memorandum is restricted to actions taken by the original manufacturer of the vehicle. Where further guidance is needed beyond the above definitions, the manufacturer’s designation of the vehicle type can be determined by researching the specific vehicle identification number (VIN). Aftermarket modifications or alterations are not a part of the vehicle design. The driver is included in the term “person” or “passenger” when determining seating capacity.
GUIDANCE ON APPLICABLE SAFETY STANDARDS ACCORDING TO VEHICLE TYPE AND USE
The chart below is provided as a guide for determining which vehicle safety standard applies to vehicles used to transport migrant or seasonal workers under MSPA. The chart is an aid and is not a substitute for the regulatory language.
| TYPE OF VEHICLE | TYPE OF USE & SAFETY STANDARD - trip 75 miles or less* | TYPE OF USE & SAFETY STANDARD - trip more than 75 miles or day haul operation |
|---|---|---|
| Passenger Automobile | 500.104 | 500.104 |
| Station Wagon | 500.104 | 500.104 |
| 1.1 Van - 10 or fewer passengers | 500.104 | 500.104 |
| 1.1 Van - more than 10 passengers | 500.104 | 500.105 |
| 1.1 Van - "windowless" cargo van | 500.104 | 500.105** |
| Bus | 500.104 | 500.105 |
| Truck/Truck Tractor/Semi-trailer | 500.104 | 500.105 |
| 1.2 Pickup Truck - workers riding only in cab | 500.104 | 500.104 |
| 1.2 Pickup Truck - workers riding in truck bed | 500.104 | 500.105 |
| Multipurpose Passenger Vehicle - not meeting truck features | 500.104 | 500.104 |
| Multipurpose Passenger Vehicle - meeting truck features | 500.104 | 500.105 |
| Low-speed Vehicle | 500.104 | 500.105 |
*The mile limitation applies to the entire trip. One trip may have numerous intermediate stops and normally ends when the vehicle returns to its starting point.
**Vans without windows or means to assure ventilation are not permitted.
GUIDANCE ON TRAILER TOWING
Towing a trailer behind any vehicle (other than a truck subject to DOT standards) transporting MSPA workers is permitted only if it meets the applicable DOL or DOT safety standards. A truck subject to DOT standards while transporting MSPA workers may not tow a trailer.
A vehicle transporting MSPA workers and towing a trailer will be examined to insure that both the vehicle and towed trailer meet the applicable safety standards. Safety standards applicable to towed trailers include the following:
When subject to DOL standards:
- external lights 29 CFR § 500.104(a)
- brakes 29 CFR § 500.104(b)
- tires 29 CFR § 500.104(c)
- safe loading 29 CFR § 500.104(k)
When subject to DOT standards:
- equipment and emergency devices 29 CFR § 500.105(b)(2)(vi)
(including trailer brake connections
and coupling devices) - safe loading 29 CFR § 500.105(b)(2)(vii)
- lighting devices and reflectors 29 CFR § 500.105(b)(2)(xi)
- parts and accessories (including 29 CFR § 500.105(b)(3)
lighting devices, brakes, and tires)
Additional safety factors to consider include, but are not limited to, whether workers were transported in the trailer and the overall safe operation of the vehicle and trailer.
Factors to consider in determining that the vehicle and trailer have been safely loaded include, but are not limited to, whether the load has been balanced from side to side and cargo weight distributed evenly along the length of the trailer; whether items have been secured and braced to prevent them from moving during travel; and for most situations, whether the trailer and tow vehicle are level (parallel to the ground) during travel (information from the trailer manufacturer may be needed to make sure this is correct for this combination of vehicles). This guidance is based on materials provided by DOT’s Federal Motor Carrier Safety Administration (FMCSA).
Some states and municipalities may have special requirements and DOT may have requirements applicable to vehicles under its jurisdiction that are towing trailers (e.g. some states require brakes on loaded trailers weighing in excess of a set amount; special permits based on the size and weight of a trailer; or additional equipment such as side view mirrors). Vehicles subject to MSPA transportation safety requirements must meet other applicable Federal and State safety standards.
Vehicles towing trailers must also carry proper insurance coverage.
