List of Goods Produced by Child Labor or Forced Labor
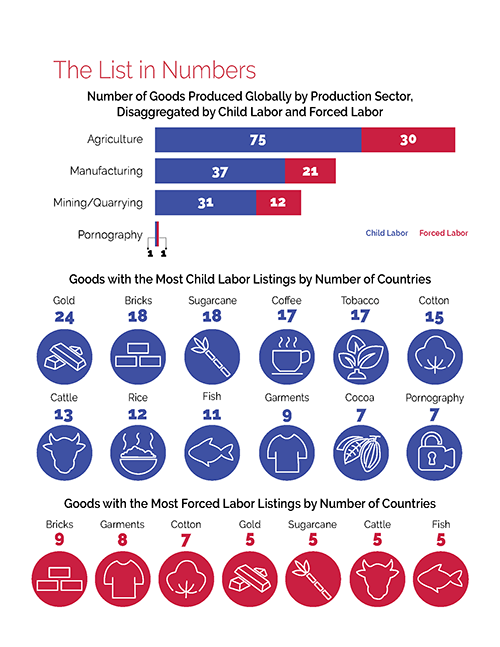
The Bureau of International Labor Affairs (ILAB) maintains a list of goods and their source countries which it has reason to believe are produced by child labor or forced labor in violation of international standards, as required under the Trafficking Victims Protection Reauthorization Act (TVPRA) of 2005 and subsequent reauthorizations. The List of Goods Produced by Child Labor or Forced Labor comprises 159 goods from 78 countries and areas, as of September 28, 2022.
ILAB maintains the List primarily to raise public awareness about forced labor and child labor around the world and to promote efforts to combat them; it is not intended to be punitive, but rather to serve as a catalyst for more strategic and focused coordination and collaboration among those working to address these problems.
Publication of the List has resulted in new opportunities for ILAB to engage with foreign governments to combat forced labor and child labor. It is also a valuable resource for researchers, advocacy organizations and companies wishing to carry out risk assessments and engage in due diligence on labor rights in their supply chains.
The countries on the List span every region of the world. The most common agricultural goods listed are sugarcane, cotton, coffee, tobacco, cattle, rice, and fish. In the manufacturing sector, bricks, garments, textiles, footwear, carpets, and fireworks appear most frequently. In mined or quarried goods, gold, coal and diamonds are most common.
ILAB published the initial TVPRA List in 2009 and updated it annually through 2014, following a set of procedural guidelines that were the product of an intensive public consultation process. ILAB now updates and publishes the List every other year, pursuant to changes in the law.
Procedural Guidelines
On January 25, 2024, ILAB's Office of Child Labor, Forced Labor, and Human Trafficking published Procedural Guidelines for the development and maintenance of the List of Goods from countries produced by child labor or forced labor in violation of international standards.
| Country/Area | Good | Exploitation Type |
|---|---|---|
| Uganda | There are reports that school-aged children harvest sand in Uganda, particularly in the Central, Eastern, and Northeastern regions of the country. According to a Government of Uganda official, sand harvesting is one of the main occupations in which child laborers work. Children harvest sand for long hours, which prevents them from attending school. Children dive underwater, scoop up sand, and transport it to boats on the river bank. This work exposes children to severe health and safety hazards, including drowning, injury, and water-borne disease. |
Child Labor |
| India | There are reports that children ages 6 to 17 produce sandstone in India. In Rajasthan, which produces 90 percent of India’s sandstone, boys and girls as young as age 6 or 7 work chiseling sandstone cobblestones, and boys ages 13 to 17 quarry sandstone. Children from migrant families or children belonging to scheduled castes, a socially disadvantaged group in India, are particularly vulnerable to child labor in producing sandstone. Based on estimates from international organizations, NGOs, and academic researchers, thousands of children work in Rajasthan’s sandstone quarries. Children working in the quarries are rarely given protective equipment such as goggles or masks, and are exposed to hazards including severe injury from stone chips; hearing loss from drilling and blasting noise; extreme heat; and inhalation of silica dust, which can lead to chronic lung disease and death. Some children also work at night or operate dangerous equipment. There are reports that adult workers are forced to work in the production of sandstone in India. Migrant workers and individuals from scheduled castes, a socially disadvantaged group in India, are especially vulnerable to forced labor in sandstone quarries. According to international organizations, NGOs, and academic researchers, incidents of forced labor and debt bondage are widespread in sandstone quarries in Rajasthan, which is the source of 90 percent of India’s sandstone. Migrant and marginalized workers are lured to the quarries with the promise of well-paying jobs, only to work in dangerous conditions for pay at a daily or per piece rate that is too low to manage basic expenses. Sandstone quarry workers are highly vulnerable to silicosis, a fatal lung disease caused by breathing the dust produced by drilling or breaking quartz-rich rocks. In many cases, quarry owners give workers advances and loans to pay for growing household and medical expenses related to silicosis. Quarry owners withhold workers’ wages as repayment for this debt, which in turn continuously accumulates due to compound interest and additional expenses. Employers record attendance informally and rarely issue written accounts of debt owed, enabling quarry owners to deduct money from the workers’ wages and inflate debts. When an indebted worker grows too ill to work or dies, this debt is transferred to his or her family, who must forfeit property or themselves labor in the quarry to pay off the debt. |
Child Labor, Forced Labor |
| Madagascar | Child Labor | |
| Burma | Forced Labor | |
| Paraguay | There is evidence that children ages 5 to 17 grow sesame in Paraguay. In 2016, the Government of Paraguay published representative results from the Survey of Activities of Rural Area Children and Adolescents 2015. The survey considers a working child to be engaged in child labor if the child is below the minimum age for employment of 14 or the child is performing work that is hazardous according to national legislation. The survey estimates that 301,827 children ages 5 to 17 perform hazardous work in rural areas of Paraguay and indicates that children working in agriculture experience accidents and illnesses, including from using dangerous tools and handling chemicals. According to the survey, almost 13 percent of Paraguayan children engaged in child labor in agriculture do not attend school. The survey estimates that 17,670 child laborers grow sesame throughout rural areas in Paraguay. Approximately 5,793 child laborers growing sesame are below the minimum age for employment in Paraguay. The survey indicates that more boys than girls are engaged in child labor producing sesame. The release of this survey demonstrates the Government of Paraguay’s commitment to addressing child labor and its acknowledgement that data collection is vital to the design and implementation of sound policies and programs. |
Child Labor |
| Brazil | There is evidence that children ages 5 to 13 raise sheep in Brazil. The ILO has found that generally children who care for farm animals may be at risk of exposure to potential health consequences, including injuries from kicks and infections from animal bites and exposure to harmful bacteria. The Government of Brazil’s 2015 National Household Survey considers all work performed by children below age 14 to be child labor. Based on an analysis of the survey, an estimated 5,773 child laborers raise sheep. The release of this survey demonstrates the Government of Brazil’s commitment to addressing child labor and its acknowledgement that data collection is vital to the design and implementation of sound policies and programs. |
Child Labor |
| Paraguay | There is evidence that children ages 5 to 17 raise sheep in Paraguay. In 2016, the Government of Paraguay published representative results from the Survey of Activities of Rural Area Children and Adolescents 2015, a representative survey of children’s work in rural areas. The survey considers a working child to be engaged in child labor if the child is below the minimum age for employment of 14 or the child is performing work that is hazardous according to national legislation. The survey estimates that 301,827 children ages 5 to 17 perform hazardous work in rural areas of Paraguay and indicates that children working in agriculture experience accidents and illnesses, including from using dangerous tools and handling chemicals. According to the survey, almost 13 percent of Paraguayan children engaged in child labor in agriculture do not attend school. The survey estimates that 9,790 child laborers raise sheep throughout rural areas in Paraguay. Approximately 4,856 child laborers raising sheep are below the minimum age for employment in Paraguay. The survey indicates that more boys than girls are engaged in child labor in sheep raising. The release of this survey demonstrates the Government of Paraguay’s commitment to addressing child labor and its acknowledgement that data collection is vital to the design and implementation of sound policies and programs. |
Child Labor |
| El Salvador | Child Labor | |
| Nicaragua | Child Labor | |
| Bangladesh | Child Labor |
your hand? Download ILAB's Sweat & Toil App today!
Are you a company looking to fight child labor and forced labor in supply
chains?